Understanding Lung Cancer
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs, the two spongy organs in your chest that take in oxygen when you inhale and release carbon dioxide when you exhale. It's one of the most common and serious types of cancer, with high morbidity and mortality rates worldwide.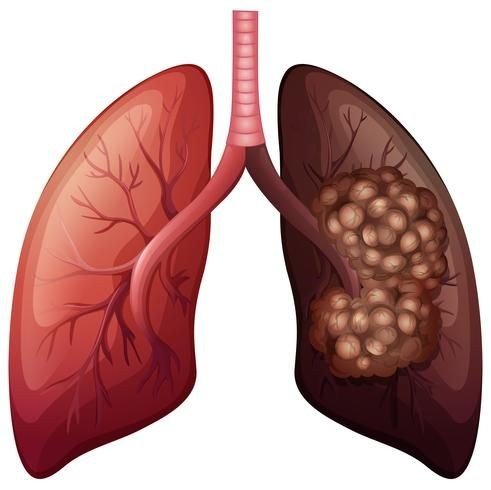
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is generally classified into two main types based on the appearance of the lung cancer cells under the microscope:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC):
- Adenocarcinoma: Starts in the cells that line the alveoli and produce mucus.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Begins in the flat cells lining the inside of the airways.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: Can appear in any part of the lung and tends to grow and spread quickly.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC):
This type accounts for about 15% of all lung cancers and is more aggressive and fast-growing. It often starts in the bronchi near the center of the chest and tends to spread widely through the body.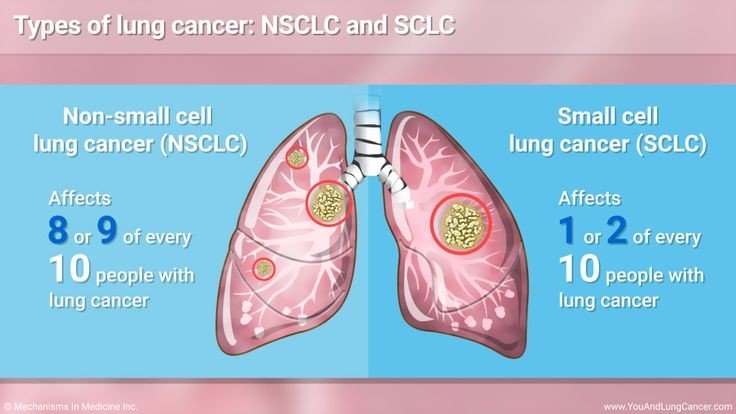
Causes of Lung Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing lung cancer:
- Smoking: The leading cause, responsible for approximately 85% of cases. Tobacco smoke contains numerous carcinogens.

- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to smoke from other people's cigarettes, cigars, or pipes.

- Radon Gas: A naturally occurring radioactive gas that can build up in homes and buildings.

- Asbestos and Other Carcinogens: Workplace exposure to asbestos and other chemicals like arsenic, nickel, and some petroleum products.

- Family History: Genetic predisposition can also play a role.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to polluted air can increase the risk.

Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer symptoms often do not appear until the disease is advanced, but they may include:
- Persistent cough
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Recurrent infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
Treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient and can include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor and some of the surrounding lung tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells, often used before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant) to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Targeted Therapy: Using drugs that specifically target cancer cell molecules.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body's immune system to fight cancer.
- Palliative Care: Managing symptoms and improving quality of life for advanced-stage cancer patients.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lung Cancer
What are the early signs of lung cancer? Early signs may include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, hoarseness, and recurrent respiratory infections. How is lung cancer diagnosed? Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests (like X-rays and CT scans), sputum cytology, and biopsy procedures to examine lung tissue. Can non-smokers get lung cancer? Yes, while smoking is the leading cause, non-smokers can develop lung cancer due to factors like radon gas, asbestos, air pollution, and genetic predisposition. What is the survival rate for lung cancer? Survival rates vary significantly depending on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Early-stage lung cancer has a higher survival rate compared to advanced stages. Can lung cancer be prevented? While not all cases can be prevented, reducing risk factors such as quitting smoking, avoiding secondhand smoke, and minimizing exposure to carcinogens can lower the risk. What are the side effects of lung cancer treatments? Side effects vary by treatment type but can include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, pain, and increased susceptibility to infections. Is lung cancer hereditary? While most lung cancers are not hereditary, a family history of lung cancer can increase the risk, suggesting a possible genetic component. What lifestyle changes can help manage lung cancer? Maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, quitting smoking, and adhering to medical advice can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.


You must be logged in to post a comment.